
In modern industrial systems, aerosol filling production lines have become indispensable equipment for industries such as cosmetics, home care, pharmaceuticals, and industrial supplies due to their high efficiency, precision, and automation. From air fresheners and personal care sprays we use daily to specialized medical inhalers, aerosol products permeate every corner of our lives. This article systematically dissects the complete process chain of a modern aerosol filling production line, revealing how raw materials are transformed into sealed, finished products. It unveils the manufacturing secrets that blend precision machinery with chemical processes.
1. Raw Material Preparation
The production process begins with the fundamental preparation of raw materials. This stage directly determines the performance and safety of the final product.
(1) Formulation Measurement and Mixing

Following strict product formulas, operators or automated systems precisely measure concentrates, solvents, active ingredients, and various additives (such as preservatives and fragrances). These materials are thoroughly and uniformly blended in sealed mixing tanks using stirring or homogenizing equipment to form the “product concentrate” ready for filling.
(2) Propellant Handling

The propellant serves as the “power source” for aerosol products. Depending on the product design (two-phase or three-phase systems), liquefied or compressed propellants (e.g., propane-butane, DME, compressed air) are stored separately and injected at specific downstream stations. Quality control (QC) of raw materials is critical at this stage, with each batch undergoing rigorous testing to ensure compliance with purity, moisture content, and other specifications.
2. Containers

Empty cans do not enter the production line directly but undergo a series of pretreatments, which form the foundation for ensuring long-term product stability.
(1) Cleaning and Purification
Empty cans enter high-speed washing machines via conveyor systems. High-pressure clean air or food-grade solvents remove contaminants like particulates and grease accumulated during transport and storage.
(2) Visual and Leak Detection
Post-cleaning, cans undergo automated visual inspection to screen out defective units with deformation, printing flaws, or stains. High-standard production lines may also perform pre-leak testing to ensure no microscopic leaks exist in the can body.
(3) Inner Coating (if required):
For highly corrosive contents or products demanding extreme purity (e.g., certain pharmaceuticals), the inner walls receive specialized epoxy or PVF coating to prevent chemical reactions between the contents and the metal can.
3. Precision Valve Insertion
The valve serves as the “heart” of the aerosol, controlling spray activation, atomization pattern, and dosage.

(1) Valve Feeding and Alignment
Valves are systematically arranged via an elevator and precisely conveyed to the crimping station.
(2) Precision Crimping
On the aerosol sealing machine, empty cans are lifted to a predetermined position. Valves are crimped onto the can mouth using precision dies. This step demands exact pressure and alignment to form a uniform, robust, and absolutely sealed mechanical structure—the first critical defense against leakage and pressure retention.
4. Filling and Pressurization
This constitutes the core filling stage of the production line, typically conducted in a sealed or negative-pressure environment to ensure safety and precision.
(1) Product Filling
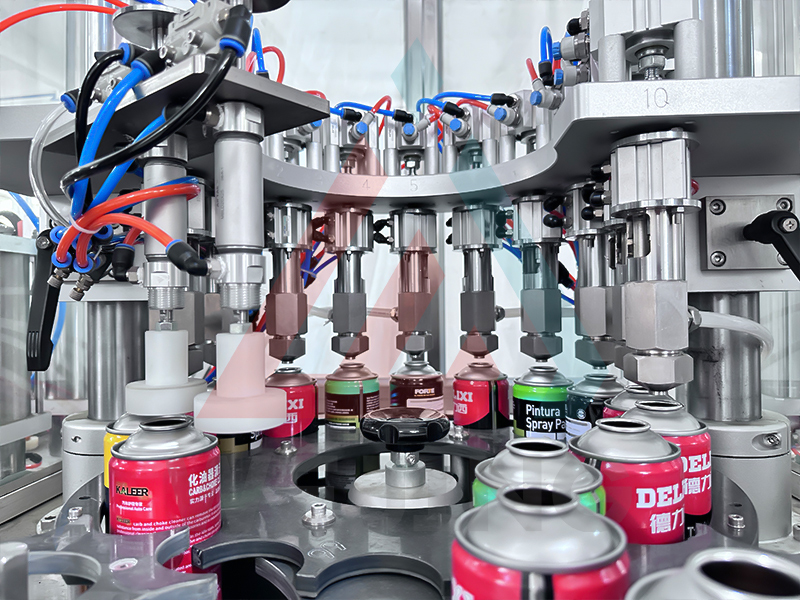

Prepared product concentrate is precisely dispensed into valve-equipped cans via volumetric filling systems (e.g., piston fillers). Filling accuracy is generally controlled within ±0.5%.
(2) Propellant Injection

This is followed by propellant filling. For liquid propellants, “pressurized filling” or “cold filling” processes are employed, injecting the propellant via filling machines. For compressed gases, specialized high-pressure filling heads are used. This process requires precise control of pressure and weight to ensure the final canister pressure meets design specifications.
5. Capping and Actuator Installation
(1) Actuator Installation
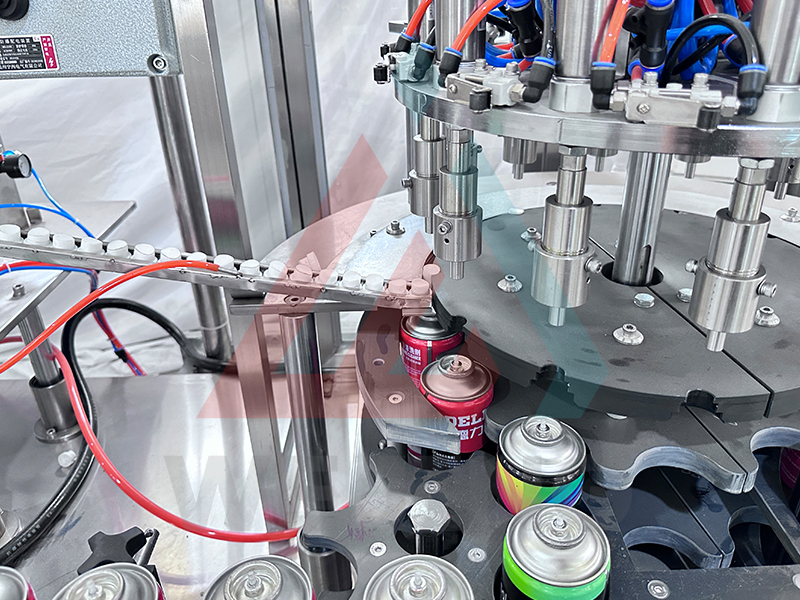
Immediately after filling and pressurization, actuators (push buttons) are pressed onto valve stems using automated equipment. In some designs, this step itself constitutes the final sealing operation.
(2) Overcap and Sealing
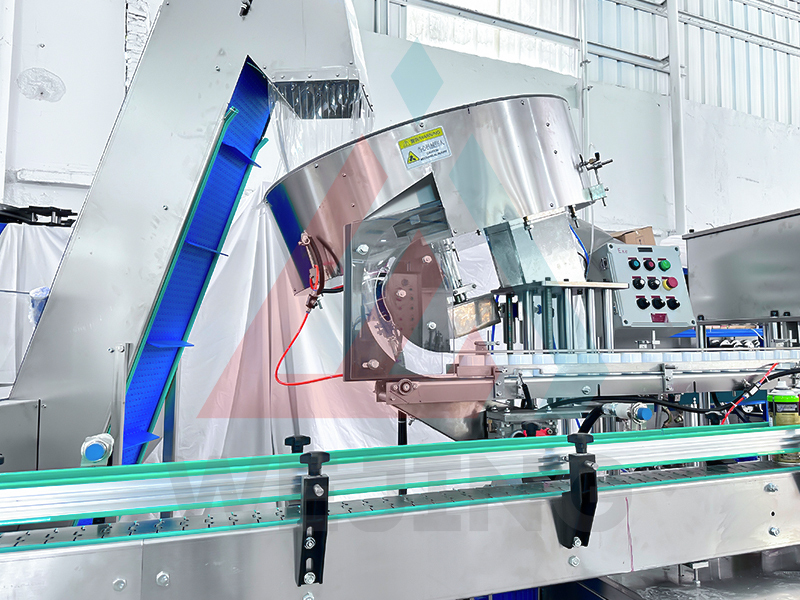

Finally, an overcap is installed to protect the actuator and prevent accidental activation, secured via snap-fit or threaded connections.
6. Testing and Inspection
Modern production lines integrate multi-tiered online detection to ensure flawless quality.
(1) Weight Leak Detection
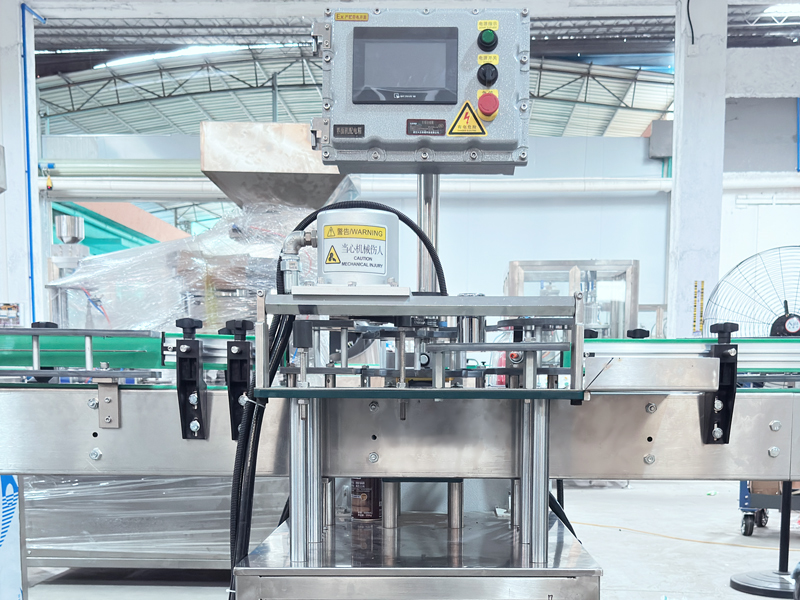

Products first pass through a weight leak detector, automatically rejecting items with non-compliant weights (indicating potential filling inaccuracies or leaks).
(2) Water Bath Leak Detection
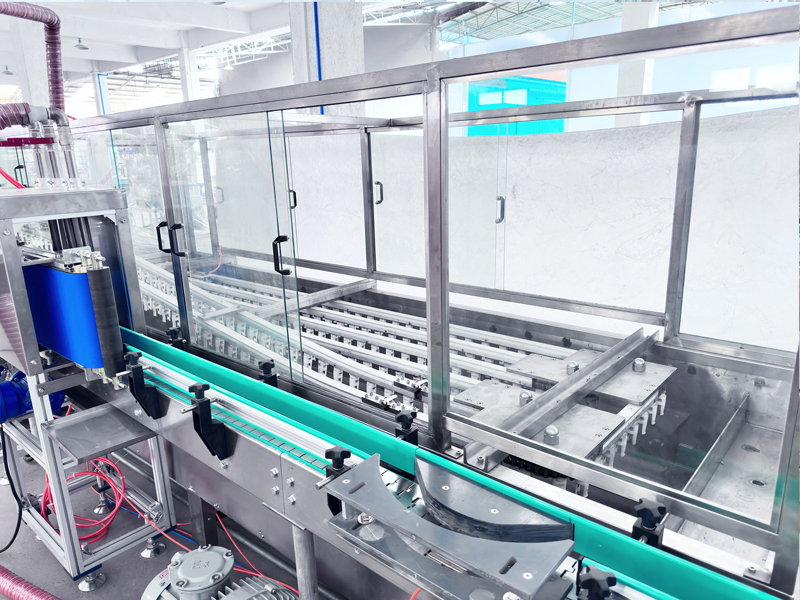

Products enter a temperature-controlled water bath leak detection tank. Heating increases internal pressure, revealing continuous bubble formation—one of the most reliable methods for sealing integrity verification.
7. Product Identification: Packaging and Traceability
(1) Coding and Labeling
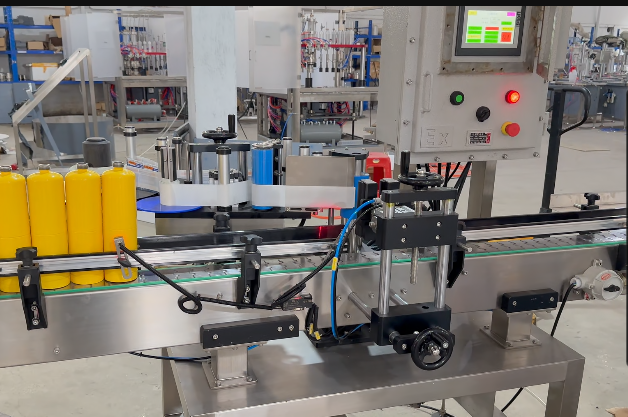

Approved cans receive laser-printed or affixed labels indicating production date and batch number.
(2) Secondary Packaging
Automated packaging lines place individual aerosol cans into color boxes, multipacks, or display trays.
(3) Cartoning and Traceability
After cartoning, boxes are affixed with barcodes containing batch information, enabling full traceability from raw materials to finished products.
Conclusion
A complete modern aerosol filling production line represents the deep integration of precision machinery, fluid control, automation, and stringent quality control. It achieves full-process automation and data-driven management—from raw material processing and high-speed filling to 100% online inspection and intelligent packaging. This not only significantly enhances production efficiency and stability but also fundamentally ensures the safety, consistency, and reliability of aerosol products. With the advancement of Industry 4.0 technologies, future aerosol production lines will continue to evolve toward greater flexibility, intelligence, and data connectivity, unlocking new innovations and possibilities for the market.













































